Stainless steel machining is a process that involves shaping, cutting, and forming stainless steel into custom parts. Stainless steel offers many advantages over other materials for machining, including its strength and durability.
Machined stainless steel parts are used in a variety of applications from medical implants to aerospace components. Choosing the right type of stainless steel for a machining project can have a significant impact on the quality and cost of the parts.
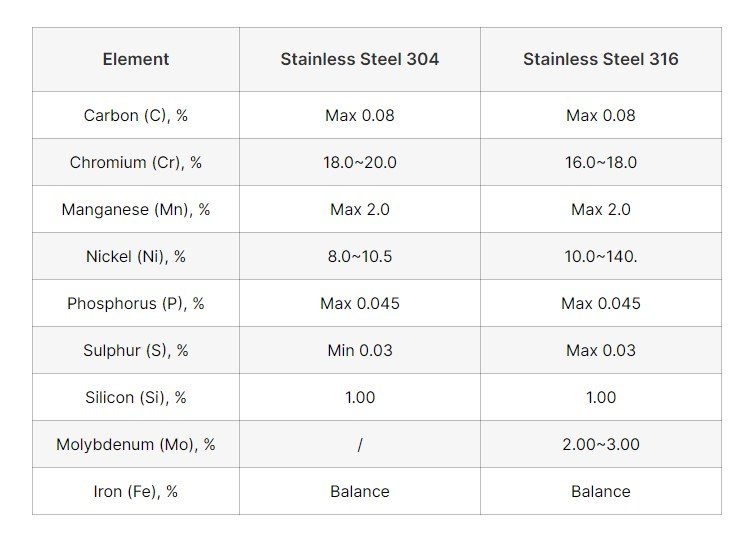
The two most popular grades of stainless steel used in machining applications are 304 and 316. Both of these grades offer excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability; however, there are some subtle differences that make them better suited to different applications.
Basics attributes of 304 Stainless Steel
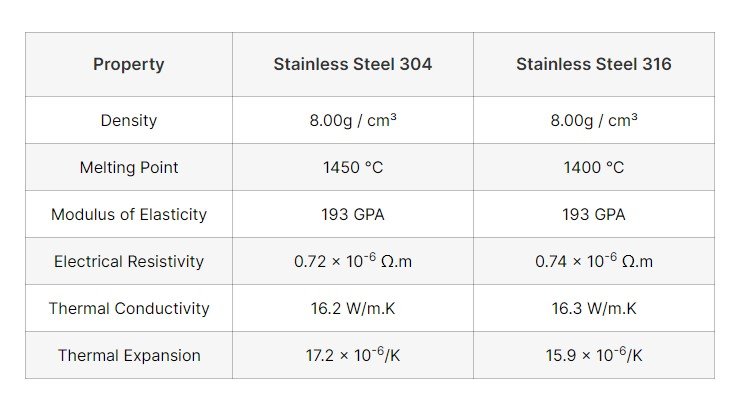
Melting Point: 1400-1450°C
Tensile Strength: 75 ksi (min)
Yield Strength: 30 ksi (min)
Elongation: 40% (min)
Density: 8 g/cm3
The most commonly machined stainless steel is 304. It has excellent weldability and formability and is commonly used for custom stainless steel parts such as brackets, frames, and other machined components.
Basics attributes of 316 Stainless Steel
Melting Point: 1450-1510°C
Tensile Strength: 75 ksi (min)
Yield Strength: 30 ksi (min)
Elongation: 40% (min)
Density: 0.29 lbs/in³
Corrosion Resistance: Excellent
316 stainless steel is more corrosion-resistant than 304 and is often used for custom-machined parts in harsh environments. It has a higher tensile strength, making it ideal for applications that require strength and durability. Additionally, 316 stainless steel provides superior resistance to pitting from acids and other corrosive agents.
The Difference Between 304SS and 316SS
Both grades are well suited for machining custom parts with tight tolerances and any surface finishes required. 304ss is an economical option with good corrosion resistance that is suitable for general-purpose applications while 316ss offers enhanced corrosion resistance at a higher cost. Below are more differences:
1) Different physical Composition
304 grade stainless contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel while 316 grade contains 16% chromium, 10% nickel, and 2% molybdenum.
2) Different Corrosion Resistance
The higher levels of molybdenum and nickel in 316SS make it more resistant to corrosion, whereas 304SS is more vulnerable to this form of attack. For this reason, 316 stainless steel is preferred when machining custom parts for use in seawater applications.
3) Different Temperature Resistance
Due to its higher molybdenum content, 316 stainless steel is better suited for high-temperature applications than 304 stainless steel. It can withstand temperatures up to 1020°F (538°C) compared to the maximum temperature of 870°F (465°C) for 304 stainless steel.
4) Different Lasting Durability
Due to its higher corrosion resistance, 316 stainless steel parts can last longer than 304 stainless steel components. Its strength and durability make it an excellent choice for machined parts that will be exposed to harsh conditions or require a long service life.
5) Different Cost
304 stainless steel is the most common grade of stainless steel used in machining applications. It offers good corrosion resistance, strength, formability, cost-effectiveness, and durability that make it a popular choice for custom parts. Due to its lower cost, 304 is often the preferred material over 316 when the price is a major factor in the selection process.
316ss is a more expensive grade of stainless steel but provides enhanced corrosion resistance due to the addition of molybdenum. Its increased resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion makes it a popular choice for applications in highly acidic or salty conditions, such as chemical processing, medical equipment, and marine environments. It is also non-magnetic but can become slightly magnetic when cold worked due to its higher levels of carbon.
6) Weldability and Formability
Both 304 and 316 stainless steel grades are weldable and formable, making them suitable for custom parts that require complex geometries. However, 316 is more resistant to heat distortion than 304 due to its higher tensile strength. This makes it an ideal material for applications that involve high temperatures or exposure to corrosive agents.
In General, when machining stainless steel parts, the right grade should be selected based on the desired performance characteristics and budget. 316ss is a more expensive grade of stainless steel but provides enhanced corrosion resistance due to the addition of molybdenum. Its increased resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion makes it a popular choice for applications in highly acidic or salty conditions, such as chemical processing, medical equipment, and marine environments. It is also non-magnetic but can become slightly magnetic when cold worked due to its higher levels of carbon.
Common Applications of 2 Grades
While both alloys are suitable for machining parts, there are differences in their chemical composition that impact the performance and longevity of the parts produced. If you are not sure what type to choose, here are the common uses for your reference:
304 Stainless Steel is often used for automotive parts, industrial fasteners, food and beverage processing, kitchen sinks, etc.

316 Stainless Steel is often used for laboratory equipment, marine hardware, chemical tanks, valves, medical equipment, and more.
Ultimately it is important to select the right grade when machining stainless steel parts in order to achieve the desired performance characteristics.
Tips to Improve The Machinability of Stainless Steel
When machining stainless steel parts, it is important to use the right cutting tools and techniques. Here are a few tips to help improve machinability:
– Use sharp tools with a positive rake angle and shear angles between 10-20 degrees.
– Increase feed rate to reduce heat build-up.
– Use plenty of coolant or lubricant while machining.
– Take shallow cuts at slow speeds to reduce stress on the tool.
– Perform chip-breaking operations regularly by using grooving or slotting cuts.
– Avoid sudden changes in temperature or direction when milling stainless steel parts.
By following these tips and selecting the appropriate grade for the application, stainless steel parts can be machined to tight tolerances and with any surface finish required. Whether you need 304ss or 316ss, custom stainless steel parts can be produced cost-effectively when the right materials and machining techniques are used.
FAQs
Q: Is 304ss or 316ss easier to machine?
A: In terms of machinability, 304ss is a bit softer than 316ss, so it can be easier to work with but may require more frequent tool changes due to its tendency to work harden. On the other hand, 316ss is more brittle than 304ss, making it more difficult to machine but less likely to suffer from tool wear. In most cases, either grade can be used for custom stainless steel machined parts with tight tolerances and any surface finishes required.
While both grades offer corrosion resistance, 316ss provides enhanced corrosion protection at a higher cost.
Q: What type of tools should I use to machine stainless steel?
A: The best tools for machining stainless steel parts are ones with a positive rake angle and shear angle between 10-20 degrees.
Q: Why is my 304 stainless steel rusting?
A: 304 stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion, however if not cared for properly or exposed to harsh conditions it can become susceptible to rusting. To prevent this from happening, be sure to regularly clean and inspect your stainless steel parts and always store them in a cool dry place away from humid environments. Additionally, you should ensure that any surface finishes are properly applied and maintained.
Q: Can 316 stainless steel be magnetic?
A: 316 stainless steel is not magnetic, however 304 can be. To test for magnetism, simply pass a strong magnet over the metal and observe if it’s attracted – if it is, then you are dealing with 304 stainless steel.
Q: Why is 316 stainless steel so expensive?
A: Due to its higher nickel content, 316 stainless steel is more expensive than 304. Additionally, it offers increased corrosion resistance, making it the ideal choice for applications where this property is necessary.
Q: What is the best grade of stainless steel?
A: The best grade of stainless steel depends on the application and desired performance characteristics. 304 and 316 are two commonly used grades, with 316 offering better corrosion resistance at a higher cost. Be sure to select the right grade for your application in order to achieve the desired performance.
Q: What is the most rust-resistant stainless steel?
A: 316 stainless steel is the most rust-resistant, followed closely by 304. However, these grades can still rust if not cared for properly or exposed to harsh conditions.

