Zinc die casting is a manufacturing process that has been used for decades to produce high-quality parts with precise dimensions. It involves the use of molten zinc, which is injected into a steel mold under pressure and then cooled to form the desired shape. This process produces parts that are strong, durable, and capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and pressures.
Zinc die casting offers several advantages over other metalworking processes, including cost savings in materials and labor as well as improved product quality. In this guide, we will explore how zinc die casting works, its benefits and drawbacks compared to other manufacturing processes, and tips for successful zinc casting projects.
What is Zinc Die Casting?
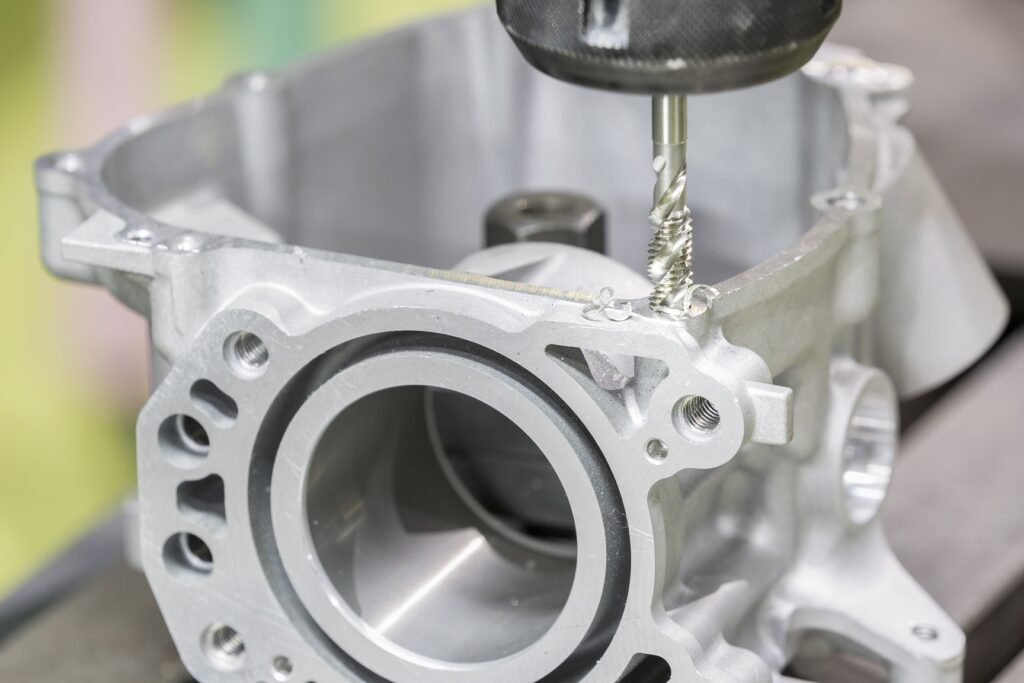

Zinc die casting is a process that involves the melting of zinc and pouring it into a mold or “die.” The molten metal solidifies within the die, forming the desired shape or product. The zinc die-casting parts are then ejected from the die and post-processed as necessary.
This process is popular in many industries for its ability to create intricate, detailed parts with a high degree of accuracy. It also offers an excellent surface finish and corrosion resistance. In addition, zinc die casting is cost-effective and relatively quick when compared to other metal casting methods.
Types of Zinc Alloys for Die Casting
The most common type of zinc alloy used for die casting is Zamak 3, also known as Zinc Alloy 3. Other popular alloys are Zamak 5 and ZA-8. Most of these alloys contain some amount of aluminum, copper, magnesium, and other elements to improve their strength and/or properties.
Zamak 3
Zamak 3 is the most widely used alloy in zinc die casting due to its excellent strength and ductility. It is also relatively inexpensive when compared to other alloys, making it a popular choice among manufacturers.
ZA-8
ZA-8 is the strongest of the three commonly used alloys and offers excellent corrosion resistance. While it is more expensive than Zamak 3 and Zamak 5, it is often used for parts that require greater strength and durability.
Zamak 5
Zamak 5 is the least expensive of the three common alloys and offers excellent ductility. It also provides a good surface finish and corrosion resistance. However, it has lower strength than Zamak 3 or ZA-8 and should not be used for parts that require greater strength.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting

Zinc die casting offers a variety of advantages over other metal casting processes, including:
• Quick production times: The process is relatively fast when compared to other metal casting processes because zinc alloys have a low melting point which will increase the cycle rate.
• Cost-effective: Due to its relative ease of use and quick cooling time, zinc die casting is generally more cost-effective than other metal casting processes. Also, this process offers an economical way to produce metal parts in large volumes.
• Complex Geometries: Zinc die casting is well-suited for producing complex geometries and intricate details with a high degree of accuracy.
• Corrosion Resistance: Zinc alloys offer good corrosion resistance, making them ideal for products that are exposed to the elements.
• Low Porosity: Zinc die-casting parts feature low porosity, ensuring a strong bond between metal and surrounding material.
• Wide Range of Applications: Due to its versatility, zinc die casting is suitable for a wide range of applications in many industries.
• Various Finishing Options: The process also allows for a variety of finishing options, from plating to powder coating, and painting.
• Fully recyclable: Unlike other metal casting processes, zinc is 100% recyclable and can be reused in the manufacturing process.
Drawbacks of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc die casting also has some drawbacks when compared to other metal casting processes, such as:
• High cost of tooling: The cost of creating a die for zinc die casting is higher than for other processes, due to the intricate nature of zinc alloys. Besides, the cost of the process can be high when dealing with smaller production runs.
• Limited sizes: The size of parts cast with zinc die casting is limited due to the low melting point of the alloy. Additionally, the process can be limited by wall thickness and the overall size of the part being produced.
• Relatively heavy: One of the main disadvantages of zinc die casting is that it produces parts that are relatively heavy, so it’s not suitable to make parts where lightweight is needed.
Overall, zinc die casting is a highly versatile and cost-effective metal casting process that offers an excellent surface finish and corrosion resistance. It is suitable for a wide range of applications in many industries due to its ability to produce intricate parts with a high degree of accuracy and relatively quick production times. However, it should be noted that there are some drawbacks to the process, such as its inability to produce lightweight parts and higher costs for smaller runs.
The Process of Zinc Die Casting
The zinc die-casting process involves the use of a die-casting machine and a metal die. The dies are usually made from hardened steel and have an exact negative impression of the part to be produced. They act as a mold into which molten zinc is injected under high pressure.
The injection process begins with melting the zinc alloy in a furnace and then pouring it into a ladle. The molten metal is kept at a constant temperature in the ladle to ensure consistent results. It is then transferred to the die-casting machine, where it is injected under high pressure into the die cavity.
The metal quickly cools and solidifies within the cavity and takes on the shape of the part. After it has cooled, the die is opened and the casted part is ejected from the die. Then It goes to trimming, which is a process of removing extra metals during die casting. After that, It undergoes secondary finishing to achieve a smooth finish, such as polishing or painting.
Application of Zinc Die Casting parts
Zinc die-casting is widely used in many industries, including automotive, electronics, medical, and power tools. It is ideal for creating complex shapes and intricate details with a high degree of accuracy.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, zinc die-casting parts are commonly used for engine components such as pistons and cylinder heads. In addition, it is also used for the production of bumpers, door handles, and other exterior components.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, zinc die-casting is commonly used for producing enclosures and housings for electronic components.
Medical Industry
Zinc die casting is often used in the medical industry to produce parts for wheelchairs, hospital beds, and other medical equipment.
Power Tools
Zinc die-casting is also used in the production of power tools such as drills, saws, and grinders. The process enables manufacturers to produce small parts with intricate details quickly and cost-effectively.
Tips for Successful Zinc Die Casting Projects
• Use the right alloy: Choosing the right zinc alloy is essential for successful die casting projects. Each alloy has its own unique properties, so it’s important to choose the one that best suits your needs.
• Design Draft Angles: Draft angles are necessary in order to ensure parts can be easily removed from the dies. It is important to include sufficient draft angles in your design to avoid issues during production.
• Allow for Contraction: Zinc shrinks as it cools, so it’s important to factor this into the design of your parts. If not accounted for, shrinkage could cause issues with part fit and function.
• Consider Post-Processing: Zinc die casting produces parts that are highly accurate and have a smooth surface finish. However, some parts will require additional post-processing operations such as polishing or painting to achieve a higher level of finish.
• Inspect molds before casting: Before production begins, it is important to inspect the molds and make sure they are in good condition. This will help prevent issues such as porosity or surface imperfections caused by worn or damaged dies.
• Maintain injection pressure: To ensure consistent results, it is important to monitor and maintain the injection pressure throughout the casting process. The pressure should be adjusted as needed in order to produce parts with precise tolerances.
• Provide proper venting: It is important to provide proper venting in the mold cavity in order to ensure smooth flow of molten metal and reduce porosity.
Overall, zinc die casting is an efficient and cost-effective process for producing complex parts with intricate details. However, it’s important to take into account the unique properties of zinc and consider factors such as alloy selection, draft angles, and post-processing operations when designing your parts. With proper planning and design, you can ensure successful die-casting projects.
FAQs About Zinc Die Casting
Q: What are the benefits of zinc die casting?
A: Zinc die casting is an efficient and cost-effective process for producing complex parts with intricate details. It allows for accurate replication of the original part design, produces a smooth surface finish, and requires minimal post-processing operations.
Q: Why is zinc used for die castings?
A: Zinc is an ideal metal for die casting because of its low melting point and high strength-to-weight ratio. It also offers good corrosion resistance and excellent electrical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Q: Can zinc parts be post-processed?
A: Yes, zinc die casting parts can be post-processed. Common post-processing operations include polishing, painting, and plating to achieve a higher level of finish.
Q: Are zinc die casting parts durable?
A: Yes, zinc die castings are very durable and have excellent wear resistance due to the high strength-to-weight ratio of the material. They are also resistant to corrosion and have good electrical properties, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Q: What is the turnaround time for zinc die casting projects?
A: The turnaround time for zinc die casting projects can vary depending on the complexity of the parts and post-processing operations required. Generally, the process takes several weeks to complete from design to finished product.
Q: Are there any tips for successful zinc die-casting projects?
A: Yes. It is important to choose the right zinc alloy, include sufficient draft angles in your design, factor in the contraction that occurs during cooling, and consider post-processing operations such as polishing or painting for a higher level of finish. With proper planning and design, you can ensure successful die-casting projects.
Q: What industries use zinc die casting?
A: Zinc die-casting is used in many industries, including automotive, electronics, medical, and power tools. It is ideal for creating complex shapes and intricate details with a high degree of accuracy.
Q: Will zinc die-casting parts rust?
A: No. Zinc is a corrosion-resistant material that does not rust or corrode easily. It can be used for outdoor applications without the need for additional coatings such as paint.
Q: How strong are zinc die-casting parts?
A: It depends on the alloy used for the casting. Zinc alloys are generally strong and durable, but some are more brittle than others. It is important to choose the right alloy for your application in order to ensure maximum strength and durability.
Q: Is zinc die-casting environmentally friendly?
A: Yes. Zinc is a recyclable material and can be reused many times over, making it an environmentally friendly option for die-casting projects. It also has low levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), so it won’t release any toxic fumes in the air.
Q: What other materials can be produced using die-casting?
A: In addition to zinc, die-casting can also be used to produce parts from aluminum, magnesium, and brass alloys. Each material has its own unique properties and is suitable for certain types of projects. It’s important to consider which material is best suited for your application when selecting a die-casting process.
Q: What Are The Benefits Of Hot Chamber Zinc Die Casting Products?
A: Hot chamber zinc die casting products offer several benefits. This method of die-casting is faster and more cost-effective than other processes since it requires less energy to melt the metal. The process also results in higher levels of accuracy and less material waste, making it an excellent choice for high-volume production runs. Additionally, hot chamber zinc die-casting allows for thinner walls and intricate details on parts that may not be possible with other processes.
Q: Challenges with Zinc Die Casting and How to Overcome Them
A: Despite its advantages, zinc die casting can also present some challenges when it comes to producing high-quality parts. Here are a few common issues faced during the production process and how to overcome them:
• Porosity and air entrapment: Porosity occurs when gases become trapped in the part during casting, resulting in weak areas or porous spots. To avoid this, it is important to monitor the pressure and temperature during production carefully.
• Cracks: Zinc is a brittle material and can easily crack during the cooling process due to contraction. Adding draft angles to your design can help prevent cracks from forming.
• Warping: This occurs when parts warp or bend due to uneven cooling. To reduce warping, it is important to ensure that all parts are cooled in an even manner, such as by using a cooling plate or hot chamber with multiple outlets.
• Blow holes: Tiny holes can form on the surface of parts due to air pockets trapped during casting. To prevent this, use a vacuum-assisted die-casting process or increase pressure levels in order to reduce the entrapment of gas bubbles.
• Fusion: Fusion occurs when two parts of a die-casting merge together during the cooling process. To avoid this, use adequate draft angles and ensure that the gap between two parts is not too small.
• Swells: Swells occur when the metal expands during casting, resulting in a part that is bigger than its original design. To reduce swells and ensure accurate parts, carefully monitor the temperature and pressure of your die-casting process.
These are just some of the issues that can arise during zinc die-casting projects and how to address them in order to produce high-quality parts. With proper setup and monitoring, zinc die-casting can be an efficient and reliable process for various projects.
This article has shed some light on the benefits and challenges of zinc die casting. If you want to learn more about this process or need help finding the right alloy for your project, get in touch with a die-casting supplier today. They will be able to provide you with advice and assistance to ensure that your finished product is of the highest quality possible.

